

Then calculate the Cumulative Count by entering this formula =B4 into the cell C4 in this case, and press Enter key.Ĥ. Sort this data in descending order by selecting the cell B4 in this case and clicking Data > Sort Largest to Smallest icon.Īnd now your values in column B are in descending order as below screenshot shown:ģ. Type and list the number of each complaints or defects of your production in a worksheet like the following screenshot:Ģ. We can create multilevel Pareto charts for each issue and can further perform another Pareto analysis on the sub-level issues and so on.To create a Pareto chart in Excel 2013 or earlier versions, please do as this:ġ.read more to verify the process changes had the desired outcome. It helps in providing an easier way to make a distinction before and after Pareto analysis Pareto Analysis Pareto analysis is a decision making technique based on the 80/20 rule where the company can achieve 80% of the project's benefits by doing the 20% of the work, or the 80% problems of the company are traced to 20 % causes.Always create the secondary y-axis with percentage descending in increments from 10 to 100.It is based on the past data, so for continuous improvement of a process, it is necessary to revamp the data on a periodic basis because the Pareto analysis is based on the historical data and doesn’t provide the forecast analysis.Before creating a Pareto chart, it is necessary to categorize the issues, and it is considered to be a good practice to keep the categories less than 10 in numbers.Pareto chart can’t be utilized to compute how awful the issue is or how far changes would bring a procedure back into specification.read more hence it cannot be used to calculate the mean, standard deviation, and other statistical values may often require. In excel, it is a function to tabulate or graphically represent the recurrence of a particular value in a group or at an interval. Pareto chart is based on the frequency distribution Frequency Distribution Frequency distribution refers to the repetitiveness of a variable, i.e., the number of times a variable occurs in a data set.So, lower levels of the Pareto chart are often required. A single cause or a reason category may further have other factors involved, so to find the major impact at each level of the problem, we have to create many Pareto charts.The Pareto chart doesn’t provide any insight into the root cause of the problem.It helps the organizational team to focus on the input that will have a greater impact in accordance with the 80/20 rule.It improves decision making in a process.Once you’ve vividly laid out these facts, you can start the planning important to take care of the issues. It also enhances problem-solving skills as it enables you to sort out business-related issues into strong facts.Once the big hitters in a process are discovered using this technique, one can move ahead for the resolutions, thus increasing the efficiency of the organization It helps to rectify the major problems and thus increases organizational efficiency.The Pareto chart highlights the major cause of the problem that hampers a process.The chart above shows that 80% of the effects come from 20% of the causes. In Axis Options, select the Maximum from Auto to fixed and enter a value 100 manually and close the format axis window Then under the axis option tab, select maximum to set it to be fixed, and set the value to 100 Click on the right-hand axis and select format axis ,.Now the Pareto chart will look like as shown below
#Create pareto chart in excel 2013 series
Select Secondary axis and close the Format Data Series window.
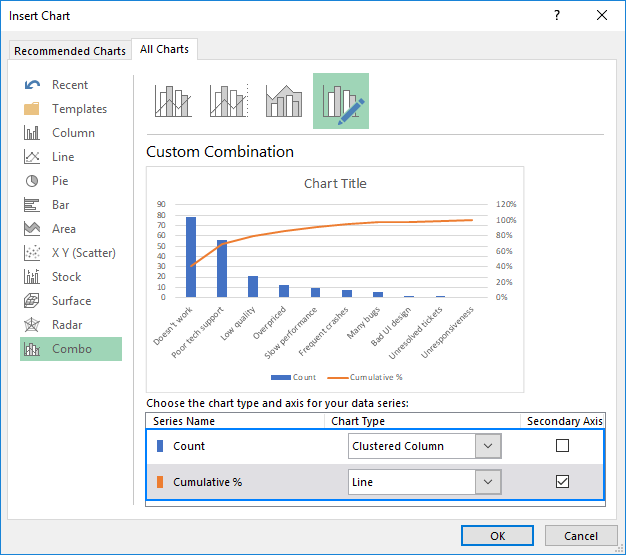
Now the Pareto chart created is shown below: Go to the Insert tab in Excel and select a 2-D column bar graph.
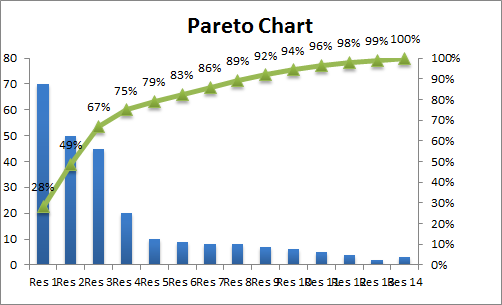
It is the method of calculating the frequency distribution and will be calculated successively by adding the percent with other frequencies. The percent will be calculated using the formula =(C3/$C$13) *100, applying throughout the other cells. Calculate the percentage of each category and further compute the cumulative percent.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
